Page 11 - Nexia SAB&T Trust Guide 2022
P. 11
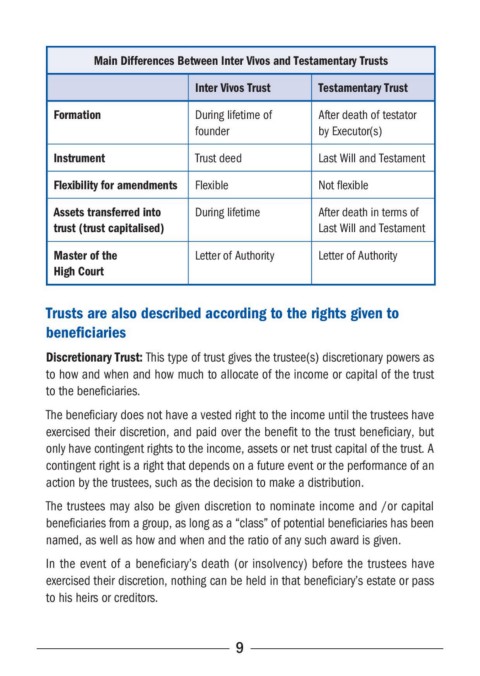
Main Differences Between Inter Vivos and Testamentary Trusts
Inter Vivos Trust Testamentary Trust
Formation During lifetime of After death of testator
founder by Executor(s)
Instrument Trust deed Last Will and Testament
Flexibility for amendments Flexible Not flexible
Assets transferred into During lifetime After death in terms of
trust (trust capitalised) Last Will and Testament
Master of the Letter of Authority Letter of Authority
High Court
Trusts are also described according to the rights given to
beneficiaries
Discretionary Trust: This type of trust gives the trustee(s) discretionary powers as
to how and when and how much to allocate of the income or capital of the trust
to the beneficiaries.
The beneficiary does not have a vested right to the income until the trustees have
exercised their discretion, and paid over the benefit to the trust beneficiary, but
only have contingent rights to the income, assets or net trust capital of the trust. A
contingent right is a right that depends on a future event or the performance of an
action by the trustees, such as the decision to make a distribution.
The trustees may also be given discretion to nominate income and /or capital
beneficiaries from a group, as long as a “class” of potential beneficiaries has been
named, as well as how and when and the ratio of any such award is given.
In the event of a beneficiary’s death (or insolvency) before the trustees have
exercised their discretion, nothing can be held in that beneficiary’s estate or pass
to his heirs or creditors.
9